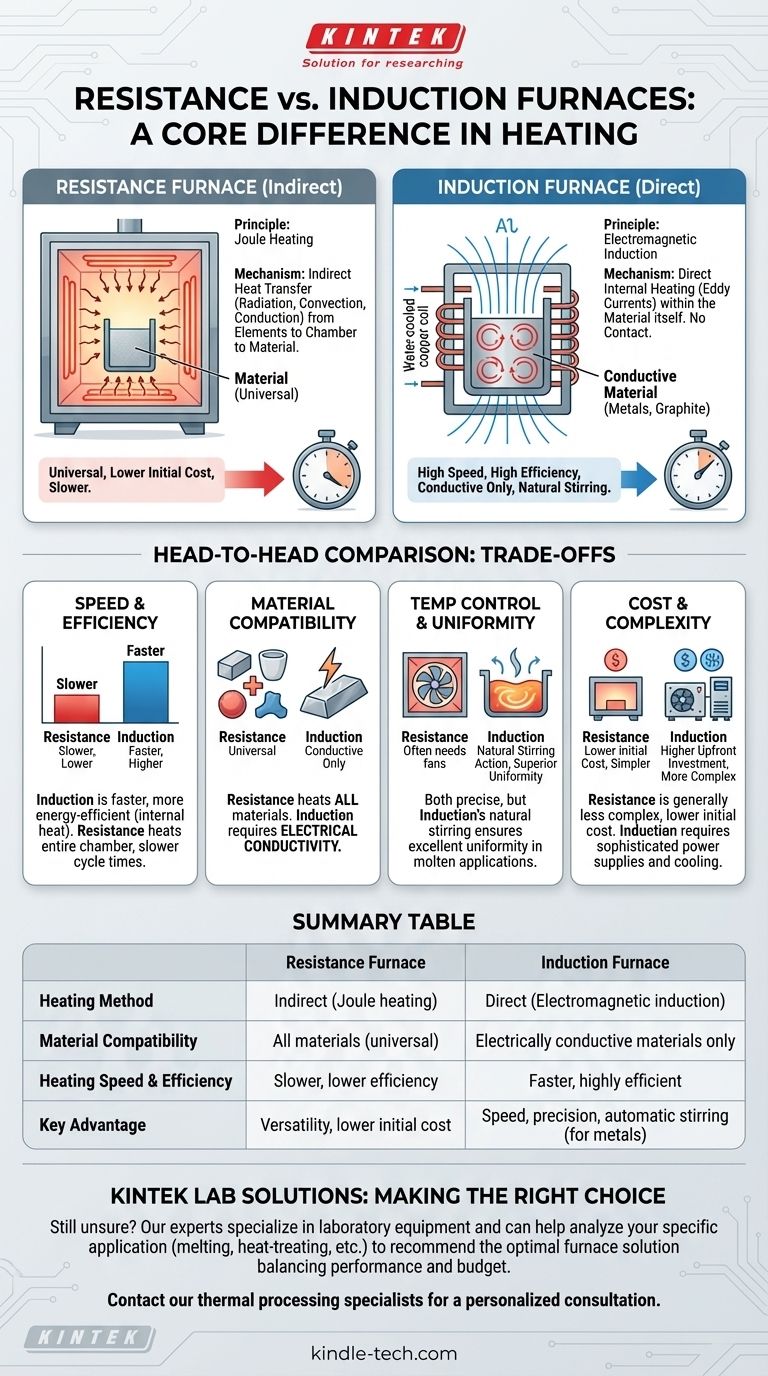
La differenza fondamentale tra un forno a resistenza e un forno a induzione risiede nel loro metodo di riscaldamento. Un forno a resistenza utilizza elementi riscaldanti che si scaldano e trasferiscono il calore al materiale indirettamente, molto simile a un forno convenzionale. Un forno a induzione, al contrario, utilizza un campo elettromagnetico per generare calore direttamente all'interno del materiale conduttivo stesso, senza contatto fisico.
La decisione fondamentale tra queste due tecnologie si riduce a un compromesso tra versatilità ed efficienza. I forni a resistenza sono lo strumento universale per riscaldare qualsiasi materiale, mentre i forni a induzione sono gli specialisti ad alta velocità e alta efficienza per materiali conduttivi come il metallo.

Come funziona un forno a resistenza
Un forno a resistenza è il tipo più comune e semplice di forno elettrico, che opera su un principio familiare a chiunque abbia usato un tostapane o un fornello elettrico.
Il Principio: Riscaldamento Joule
Il meccanismo si basa sulla resistenza elettrica. Una corrente elettrica elevata viene fatta passare attraverso un elemento riscaldante appositamente progettato, realizzato con un materiale ad alta resistenza.
Questa resistenza al flusso di elettricità fa sì che l'elemento diventi estremamente caldo, un effetto noto come riscaldamento Joule.
Il Meccanismo: Trasferimento di calore indiretto
Il calore intenso di questi elementi viene quindi trasferito al materiale all'interno del forno. Ciò avviene attraverso una combinazione di radiazione, convezione e conduzione.
In sostanza, il forno riscalda l'atmosfera e le pareti della camera, che a loro volta riscaldano il materiale target. È un processo di riscaldamento indiretto.
Caratteristiche chiave
I forni a resistenza sono noti per la loro versatilità, poiché possono riscaldare qualsiasi tipo di materiale, sia esso conduttivo o meno. Sono generalmente più semplici nel design e meno costosi inizialmente.
Come funziona un forno a induzione
Il riscaldamento a induzione è un metodo più avanzato, mirato ed efficiente che cambia fondamentalmente il modo in cui l'energia termica viene fornita a un materiale.
Il Principio: Induzione Elettromagnetica
Un forno a induzione utilizza una potente bobina per generare un campo magnetico che si alterna rapidamente. Quando un materiale conduttivo (come acciaio o grafite) viene posto all'interno di questo campo, il campo induce correnti elettriche all'interno del materiale stesso.
Queste piccole correnti circolari sono note come correnti parassite.
Il Meccanismo: Riscaldamento Interno Diretto
La resistenza naturale del materiale a queste correnti parassite genera calore preciso e rapido dall'interno verso l'esterno. Non sono necessari elementi riscaldanti esterni.
Il calore viene generato direttamente all'interno del pezzo, rendendo il processo estremamente veloce ed efficiente, poiché pochissima energia viene sprecata per riscaldare lo spazio circostante.
Caratteristiche chiave
Un vantaggio unico del riscaldamento a induzione per i metalli fusi è l'azione di agitazione naturale causata dai campi magnetici. Ciò garantisce un'eccellente uniformità di temperatura e miscelazione della lega senza agitatori meccanici.
Comprendere i compromessi: un confronto diretto
La scelta del forno giusto richiede la comprensione dei distinti vantaggi e limitazioni inerenti a ciascun metodo di riscaldamento.
Velocità ed Efficienza di Riscaldamento
I forni a induzione sono significativamente più veloci e più efficienti dal punto di vista energetico. Poiché il calore viene generato internamente, la temperatura target viene raggiunta in una frazione del tempo e meno energia viene persa nell'ambiente.
I forni a resistenza devono prima riscaldare gli elementi e l'intera camera del forno, con conseguenti tempi di ciclo più lenti e una minore efficienza complessiva.
Compatibilità dei Materiali
I forni a resistenza sono universali. Possono riscaldare metalli, ceramiche, polimeri e compositi senza problemi, poiché il loro funzionamento non dipende dalle proprietà elettriche del materiale.
I forni a induzione sono specialisti. Sono altamente efficaci ma possono riscaldare solo materiali elettricamente conduttivi.
Controllo e Uniformità della Temperatura
Entrambi i tipi possono raggiungere alti livelli di controllo della temperatura. Tuttavia, l'effetto di agitazione naturale in un forno a induzione fornisce una maggiore uniformità termica nelle applicazioni di metallo fuso.
Nei forni a resistenza, raggiungere un'elevata uniformità spesso richiede ventilatori per far circolare l'atmosfera, il che aggiunge complessità.
Costo e Complessità
I forni a resistenza sono generalmente meno complessi e hanno un costo iniziale inferiore. La loro manutenzione è spesso più semplice e meno costosa nel corso della loro vita utile.
I forni a induzione sono sistemi più complessi, che richiedono alimentatori e sistemi di raffreddamento sofisticati, il che si traduce in un investimento iniziale più elevato.
Fare la scelta giusta per la tua applicazione
La tua decisione finale dovrebbe essere interamente guidata dal tuo materiale specifico, dai requisiti di processo e dal budget.
- Se il tuo obiettivo principale è la versatilità e un costo iniziale inferiore: Un forno a resistenza è la scelta superiore, fungendo da cavallo di battaglia affidabile per un'ampia varietà di materiali e applicazioni.
- Se il tuo obiettivo principale è la velocità, l'efficienza energetica e la lavorazione di metalli conduttivi: Un forno a induzione offre prestazioni ineguagliabili, specialmente per la fusione, la brasatura o il trattamento termico ad alta velocità.
- Se stai lavorando con materiali non conduttivi come le ceramiche: Un forno a resistenza è la tua unica opzione praticabile.
- Se hai bisogno di agitazione automatica di un bagno di metallo fuso: L'agitazione elettromagnetica intrinseca di un forno a induzione è un importante vantaggio operativo.
Comprendere questa differenza fondamentale nel meccanismo di riscaldamento è la chiave per selezionare lo strumento più efficace per il tuo specifico compito di lavorazione termica.
Tabella riassuntiva:
| Caratteristica | Forno a Resistenza | Forno a Induzione |
|---|---|---|
| Metodo di Riscaldamento | Indiretto (Riscaldamento Joule) | Diretto (Induzione elettromagnetica) |
| Compatibilità Materiali | Tutti i materiali (universale) | Solo materiali elettricamente conduttivi |
| Velocità ed Efficienza di Riscaldamento | Più lento, minore efficienza | Più veloce, altamente efficiente |
| Vantaggio Chiave | Versatilità, costo iniziale inferiore | Velocità, precisione, agitazione automatica (per metalli) |
Ancora incerto su quale forno sia giusto per i materiali e i processi specifici del tuo laboratorio?
KINTEK è specializzata in attrezzature e materiali di consumo da laboratorio. I nostri esperti possono aiutarti ad analizzare i requisiti della tua applicazione — sia che tu stia fondendo metalli, trattando termicamente leghe o lavorando ceramiche — per raccomandare la soluzione di forno ottimale che bilanci prestazioni, efficienza e budget.
Contatta oggi i nostri specialisti di lavorazione termica per una consulenza personalizzata e scopri come il forno giusto può migliorare la produttività e i risultati del tuo laboratorio.
Guida Visiva
Prodotti correlati
- Fornace a tubo da laboratorio ad alta temperatura da 1400℃ con tubo in allumina
- Fornace a Tubo da Laboratorio ad Alta Temperatura da 1700℃ con Tubo di Allumina
- Fornace a Tubo Verticale da Laboratorio
- Fornace a Tubo al Quarzo per Trattamento Termico Rapido (RTP) da Laboratorio
- Fornace a muffola da 1800℃ per laboratorio
Domande frequenti
- Come un forno tubolare ad alta temperatura facilita la trasformazione di fase dei prodotti di allumina? Controllo Termico Avanzato
- Come facilita un tubo di quarzo la condensazione frazionata in un forno di gassificazione sottovuoto a tubo orizzontale? Guida esperta
- Come pulire un forno a tubo? Una guida passo passo per una manutenzione sicura ed efficace
- A cosa serve un forno tubolare? Riscaldamento di precisione per la sintesi e l'analisi dei materiali
- Perché viene utilizzato un forno a tubo di quarzo nell'ossidazione termica dei rivestimenti di MnCr2O4? Sblocca un'ossidazione selettiva precisa



















