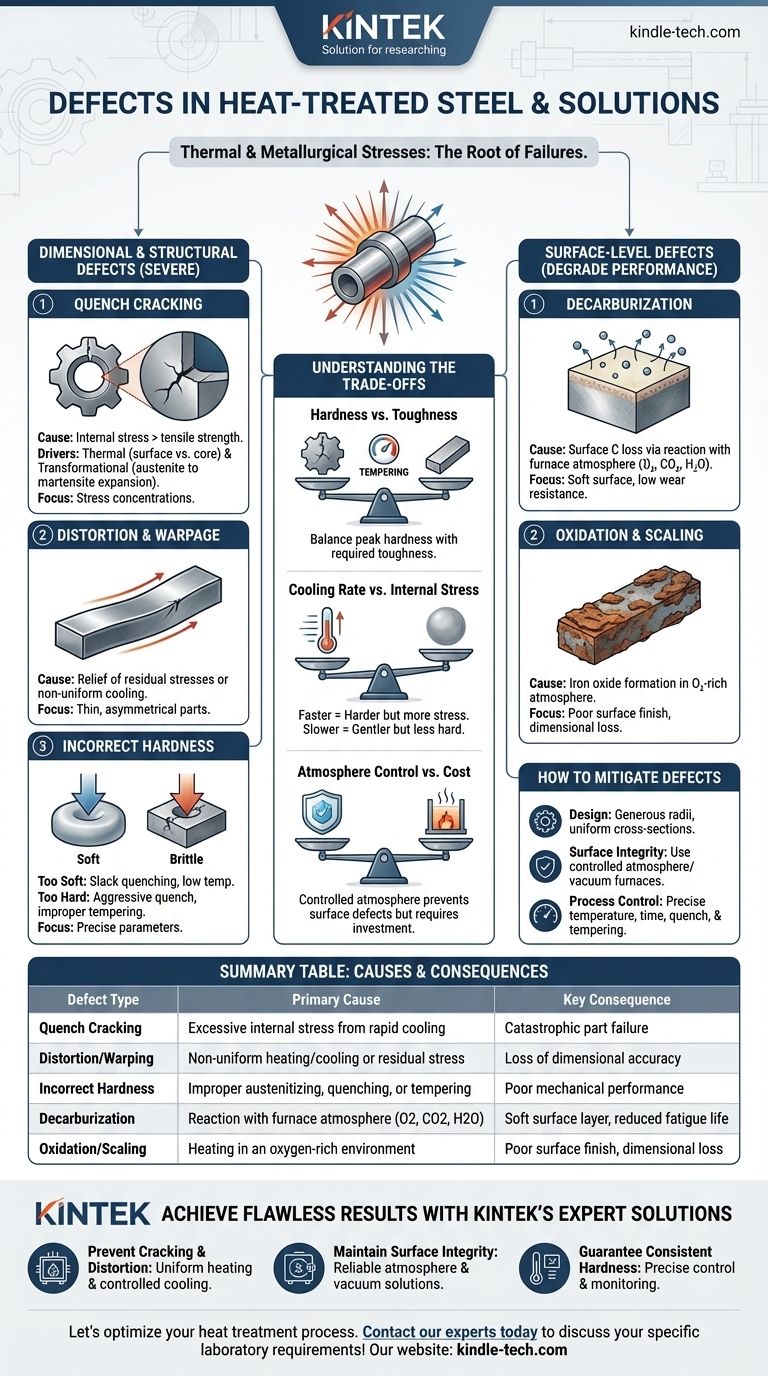
I difetti nell'acciaio trattato termicamente sono causati principalmente dalle immense sollecitazioni termiche e metallurgiche introdotte durante il riscaldamento e il raffreddamento rapido. I difetti più comuni sono cricche, distorsione (deformazione), cambiamenti indesiderati della superficie come la decarburazione e la formazione di scaglie, e l'incapacità di raggiungere la durezza o la microstruttura desiderata. Questi fallimenti non sono casuali, ma sono conseguenze dirette di parametri di processo controllati in modo improprio.
I difetti del trattamento termico sono risultati prevedibili di stress termico, trasformazioni di fase e reazioni chimiche atmosferiche. La loro prevenzione dipende dal controllo rigoroso della velocità di variazione della temperatura, dell'atmosfera del forno e della geometria del pezzo fin dalla fase di progettazione.

Guasti Dimensionali e Strutturali
I difetti più gravi compromettono l'integrità meccanica e l'accuratezza dimensionale del componente, rendendolo spesso inutilizzabile.
Cricche da Tempra (Quench Cracking)
Le cricche da tempra sono il difetto più critico nel trattamento termico. Si verificano quando le sollecitazioni interne dovute alla tempra superano la resistenza a trazione ultima del materiale.
Ciò è guidato da due forze principali: lo stress termico derivante dal raffreddamento della superficie molto più velocemente del nucleo, e lo stress trasformazionale dovuto all'espansione che si verifica quando l'austenite si trasforma in martensite fragile.
Le cricche originano tipicamente in punti di concentrazione dello stress come angoli vivi, cave per chiavi o cambiamenti improvvisi nella sezione trasversale del pezzo.
Distorsione e Deformazione (Warping)
La distorsione è un cambiamento irreversibile nelle dimensioni o nella forma di un componente che si verifica durante il trattamento termico.
Ciò è spesso causato dal rilascio delle sollecitazioni residue impresse durante le fasi precedenti di lavorazione (come la lavorazione meccanica) o da un riscaldamento e raffreddamento non uniformi. I pezzi sottili, lunghi o asimmetrici sono particolarmente suscettibili alla deformazione.
Durezza Errata
Ottenere la durezza corretta è spesso l'obiettivo primario, e il fallimento in questo può essere dovuto a diversi fattori.
Un pezzo troppo tenero può derivare da una temperatura o un tempo di austenitizzazione insufficienti, o da una tempra troppo lenta per la temprabilità dell'acciaio (nota come tempra debole o "slack quenching").
Al contrario, un pezzo troppo duro e fragile è spesso il risultato di una tempra eccessivamente aggressiva o, più comunemente, di una fase di rinvenimento impropria o mancata dopo la tempra.
Difetti a Livello Superficiale
Questi difetti degradano la superficie dell'acciaio, compromettendone le prestazioni in applicazioni che richiedono elevata resistenza all'usura o alla fatica.
Decarburazione
La decarburazione è la perdita di carbonio dalla superficie dell'acciaio. Questo è un problema significativo perché il carbonio è l'elemento principale responsabile della durezza nell'acciaio.
È causata da una reazione chimica tra l'acciaio e l'atmosfera del forno (ossigeno, anidride carbonica, vapore acqueo) ad alte temperature. Il risultato è uno strato superficiale morbido e debole che riduce drasticamente la resistenza all'usura e la vita a fatica.
Ossidazione e Formazione di Scaglie (Scaling)
L'ossidazione è la formazione di uno strato di ossido di ferro (scaglia) sulla superficie del componente quando riscaldato in un'atmosfera ricca di ossigeno.
Questa scaglia provoca una finitura superficiale scadente e una perdita di accuratezza dimensionale. Può anche isolare il pezzo, portando a una tempra non uniforme e potenzialmente mascherando difetti sottostanti più gravi come le cricche da tempra.
Comprendere i Compromessi
La selezione di un processo di trattamento termico comporta sempre il bilanciamento di fattori in competizione. Comprendere questi compromessi è fondamentale per prevenire i difetti.
Durezza vs. Tenacità
Il compromesso fondamentale nel trattamento termico è che i processi che creano durezza estrema, come la tempra, creano anche una microstruttura fragile (martensite non rinvenuta).
Il rinvenimento è la fase post-tempra essenziale che riduce questa fragilità e le sollecitazioni interne, conferendo tenacità. Tuttavia, questo processo riduce anche la durezza di picco. L'arte sta nel trovare l'equilibrio preciso richiesto per l'applicazione.
Velocità di Raffreddamento vs. Sollecitazione Interna
Una velocità di raffreddamento più rapida è più efficace nell'ottenere la piena durezza, specialmente negli acciai a basso tenore di lega.
Tuttavia, una tempra rapida (ad esempio, utilizzando acqua o salamoia) genera enormi gradienti termici e sollecitazioni interne, aumentando drasticamente il rischio di distorsione e cricche. Una tempra più lenta (ad esempio, utilizzando olio o gas) è più delicata ma potrebbe non raggiungere la durezza massima.
Controllo dell'Atmosfera vs. Costo
L'utilizzo di un'atmosfera controllata (come vuoto, azoto o argon) previene completamente la decarburazione e l'ossidazione, producendo un pezzo pulito e brillante.
Questi processi, tuttavia, richiedono attrezzature più sofisticate e costose rispetto al riscaldamento in un forno ad aria aperta. Il costo deve essere giustificato dai requisiti superficiali del componente.
Come Mitigare i Difetti del Trattamento Termico
La prevenzione dei difetti richiede un approccio sistematico incentrato sulla progettazione, la selezione dei materiali e il controllo preciso del processo.
- Se la vostra attenzione principale è prevenire cricche e distorsioni: Progettare pezzi con raggi ampi e sezioni uniformi e selezionare un mezzo di tempra meno severo appropriato per la temprabilità dell'acciaio.
- Se la vostra attenzione principale è mantenere l'integrità superficiale: Utilizzare forni a atmosfera controllata (ad esempio, sottovuoto, gas inerte) o rivestimenti protettivi per prevenire la decarburazione e la formazione di scaglie.
- Se la vostra attenzione principale è ottenere una durezza costante: Assicurare un controllo preciso della temperatura di austenitizzazione, del tempo di mantenimento e dell'agitazione durante la tempra, e seguire sempre un ciclo di rinvenimento appropriato.
Un trattamento termico di successo è un processo ingegneristico controllato in cui la lungimiranza nella progettazione e la precisione nell'esecuzione determinano la qualità finale del componente.
Tabella Riassuntiva:
| Tipo di Difetto | Causa Principale | Conseguenza Chiave |
|---|---|---|
| Cricche da Tempra | Stress interno eccessivo dovuto al raffreddamento rapido | Guasto catastrofico del pezzo |
| Distorsione/Deformazione | Riscaldamento/raffreddamento non uniforme o stress residuo | Perdita di accuratezza dimensionale |
| Durezza Errata | Austenitizzazione, tempra o rinvenimento impropri | Scarse prestazioni meccaniche |
| Decarburazione | Reazione con l'atmosfera del forno (O2, CO2, H2O) | Strato superficiale morbido, ridotta vita a fatica |
| Ossidazione/Scagliatura | Riscaldamento in ambiente ricco di ossigeno | Finitura superficiale scadente, perdita dimensionale |
Ottieni Risultati Impeccabili con le Soluzioni Esperte di KINTEK
Elimina i costosi difetti del trattamento termico e assicurati che i tuoi componenti in acciaio soddisfino i più alti standard di durezza, durata e accuratezza dimensionale. KINTEK è specializzata in attrezzature e materiali di consumo di laboratorio premium, fornendo i forni precisi, i sistemi di controllo dell'atmosfera e il supporto esperto di cui il tuo laboratorio ha bisogno per perfezionare la sua lavorazione termica.
Ti aiutiamo a:
- Prevenire Cricche e Distorsioni: Con attrezzature progettate per un riscaldamento uniforme e un raffreddamento controllato.
- Mantenere l'Integrità Superficiale: Attraverso soluzioni affidabili di forni sottovuoto e a atmosfera controllata.
- Garantire una Durezza Costante: Con un controllo preciso della temperatura e strumenti di monitoraggio, e seguendo sempre un ciclo di rinvenimento adeguato.
Ottimizziamo il tuo processo di trattamento termico. Contatta oggi i nostri esperti per discutere le esigenze specifiche del tuo laboratorio!
Guida Visiva
Prodotti correlati
- Fornace per Trattamento Termico Sottovuoto con Rivestimento in Fibra Ceramica
- Fornace per trattamento termico e sinterizzazione sottovuoto di tungsteno a 2200 ℃
- Fornace per Trattamento Termico Sottovuoto e Fornace per Fusione a Induzione a Levitazione
- Fornace a vuoto di molibdeno per trattamento termico
- Fornace per brasatura sinterizzata a trattamento termico sotto vuoto
Domande frequenti
- Qual è la temperatura massima in un forno a vuoto? Dipende dai materiali e dalle esigenze del processo
- A cosa serve un forno a vuoto? Sblocca la purezza nella lavorazione ad alta temperatura
- Quali sono i vantaggi della tempra sottovuoto? Ottenere precisione e pulizia superiori per componenti critici
- Perché si esegue il trattamento termico sotto vuoto? Ottenere componenti metallici impeccabili e ad alte prestazioni
- A cosa servono i forni a vuoto? Sblocca la massima purezza e prestazioni dei materiali



















