Alla sua base, lo sputtering è un processo fisico utilizzato per depositare strati di materiale eccezionalmente sottili e uniformi su una superficie. Funziona creando un plasma in un vuoto e utilizzando ioni energizzati da questo plasma per staccare fisicamente gli atomi da un materiale sorgente, noto come "bersaglio". Questi atomi dislocati viaggiano quindi e rivestono un oggetto di destinazione, o "substrato", formando un film sottile altamente controllato.
Lo sputtering non è semplicemente "spruzzare" atomi. È una tecnica di deposizione sotto vuoto altamente controllata in cui un gas inerte viene ionizzato per creare un plasma. Questi ioni vengono quindi accelerati per bombardare un bersaglio, staccando gli atomi tramite trasferimento di quantità di moto fisico, che poi si depositano su un substrato per formare un film sottile preciso.
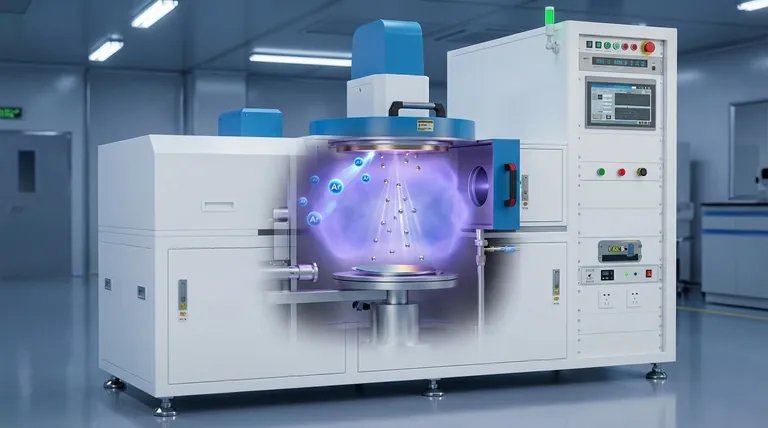
L'anatomia del processo di sputtering
Per capire come funziona lo sputtering, è necessario innanzitutto riconoscere i suoi componenti chiave, che operano in un ambiente attentamente controllato.
La camera a vuoto
L'intero processo si svolge all'interno di una camera a vuoto sigillata. La rimozione dell'aria e di altri gas reattivi è fondamentale per prevenire la contaminazione del film e per consentire agli atomi spruzzati di viaggiare liberamente dal bersaglio al substrato.
Il bersaglio
Il bersaglio è una lastra solida del materiale che si desidera depositare. Agisce come sorgente per il film sottile. Una carica negativa ad alta tensione viene applicata al bersaglio, rendendolo un catodo.
Il substrato
Questo è l'oggetto o il materiale che verrà rivestito. È posizionato strategicamente per intercettare il flusso di atomi espulsi dal bersaglio.
Il gas di sputtering
Un gas inerte, più comunemente Argon (Ar), viene introdotto nella camera a una pressione molto bassa. Questo gas non fa parte del film finale; invece, serve come "munizione" per il processo di bombardamento.
Il meccanismo di sputtering, passo dopo passo
Il processo si svolge in una sequenza precisa, trasformando un bersaglio solido in un vapore atomico che costruisce un nuovo film.
Fase 1: Creazione del plasma
Dopo aver introdotto il gas Argon, viene applicato un forte campo elettrico. Gli elettroni liberi nella camera vengono accelerati da questo campo e collidono con gli atomi neutri di Argon, staccando un elettrone dall'atomo di Argon.
Questo crea uno ione Argon caricato positivamente (Ar+) e un altro elettrone libero, che può quindi ionizzare più atomi di Argon. Questa reazione a catena sostiene uno stato di materia incandescente ed energizzato noto come plasma—una miscela di ioni positivi, elettroni e atomi neutri.
Fase 2: Bombardamento ionico
Gli ioni Argon caricati positivamente (Ar+) sono fortemente attratti dal bersaglio caricato negativamente. Accelerano verso il bersaglio ad alta velocità, acquisendo una significativa energia cinetica.
Fase 3: Espulsione atomica tramite trasferimento di quantità di moto
Quando questi ioni ad alta energia colpiscono la superficie del bersaglio, trasferiscono la loro quantità di moto agli atomi del bersaglio in un processo simile a una collisione di palle da biliardo. Questo impatto iniziale innesca una cascata di collisioni all'interno dei primi strati atomici del materiale del bersaglio.
Se questa cascata dirige abbastanza energia verso la superficie—una quantità maggiore dell'energia di legame superficiale del materiale—un atomo del bersaglio viene fisicamente staccato ed espulso dalla superficie. Questo atomo espulso è ciò che chiamiamo "spruzzato".
Fase 4: Deposizione e crescita del film
Gli atomi spruzzati viaggiano in linea retta attraverso il vuoto finché non colpiscono il substrato. Al loro arrivo, aderiscono alla superficie (un processo chiamato adsorbimento) e iniziano ad accumularsi, strato dopo strato.
Nel tempo, questo accumulo di atomi forma un film sottile continuo, denso e altamente aderente sulla superficie del substrato.
Comprendere i compromessi e i fattori di controllo
Le proprietà finali del film spruzzato non sono accidentali; sono il risultato diretto del controllo dei parametri chiave del processo. Comprendere questi compromessi è essenziale per ottenere il risultato desiderato.
Pressione del gas
L'abbassamento della pressione del gas riduce la possibilità che gli atomi spruzzati collidano con gli atomi di gas sulla loro strada verso il substrato. Ciò si traduce in un film più denso e di qualità superiore, ma spesso diminuisce il tasso di deposizione. Al contrario, una pressione più alta può aumentare il tasso di deposizione ma può portare a film più porosi.
Potenza e tensione del bersaglio
L'aumento della tensione (e quindi della potenza) applicata al bersaglio aumenta l'energia degli ioni bombardanti. Ciò aumenta la resa di sputtering—il numero di atomi espulsi per ione in ingresso—risultando in un tasso di deposizione più veloce. Tuttavia, una potenza eccessiva può causare un riscaldamento indesiderato del substrato e del bersaglio.
Scelta del gas
La massa dello ione del gas inerte influenza l'efficienza del trasferimento di quantità di moto. Gas più pesanti come il Cripto (Kr) o lo Xeno (Xe) sono più efficienti nello sputtering di materiali bersaglio pesanti rispetto all'Argon, portando a tassi di deposizione più elevati. Tuttavia, sono anche significativamente più costosi.
Geometria del sistema
La distanza e l'orientamento tra il bersaglio e il substrato hanno un impatto importante sull'uniformità e sullo spessore del film. Una distanza più breve può aumentare la velocità ma può ridurre l'uniformità su un substrato di grandi dimensioni.
Applicare questo al tuo obiettivo
La versatilità dello sputtering deriva dalla tua capacità di regolare questi parametri per ottenere un risultato specifico.
- Se il tuo obiettivo principale è un alto tasso di deposizione: Aumenta la potenza applicata al bersaglio e considera l'utilizzo di un gas inerte più pesante come il Cripto per massimizzare il trasferimento di quantità di moto.
- Se il tuo obiettivo principale è la qualità e la densità del film: Utilizza una pressione del gas più bassa per garantire che gli atomi spruzzati percorrano un percorso chiaro e mantieni un controllo preciso sulla temperatura del substrato.
- Se il tuo obiettivo principale è rivestire una lega complessa: Lo sputtering è ideale, poiché il meccanismo di espulsione fisica generalmente preserva i rapporti elementari dal bersaglio al film.
- Se il tuo obiettivo principale è l'adesione: Lo sputtering fornisce un'eccellente adesione del film perché gli atomi in arrivo hanno abbastanza energia per incastrarsi leggermente nella superficie del substrato, creando un forte legame.
Padroneggiando questi principi fondamentali, puoi sfruttare lo sputtering per ingegnerizzare superfici con specifiche proprietà ottiche, elettriche o meccaniche a livello atomico.
Tabella riassuntiva:
| Componente chiave | Ruolo nel processo di sputtering |
|---|---|
| Camera a vuoto | Fornisce un ambiente privo di contaminazioni per il viaggio degli atomi. |
| Bersaglio (Catodo) | Materiale sorgente che viene bombardato per rilasciare atomi di rivestimento. |
| Substrato | L'oggetto o la superficie che riceve il rivestimento a film sottile. |
| Gas di sputtering (es. Argon) | Ionizzato per creare plasma per bombardare il bersaglio. |
| Plasma | Una miscela di ioni ed elettroni che energizza il processo di sputtering. |
Pronto a ingegnerizzare superfici con film sottili di precisione? KINTEK è specializzata in attrezzature e materiali di consumo da laboratorio per sputtering e altre tecniche di deposizione. La nostra esperienza aiuta i laboratori a ottenere adesione, densità e uniformità superiori del film. Che tu stia sviluppando semiconduttori, rivestimenti ottici o materiali avanzati, forniamo le attrezzature affidabili e il supporto di cui hai bisogno. Contatta i nostri esperti oggi stesso per discutere la tua applicazione specifica e scoprire come KINTEK può migliorare le tue capacità di ricerca e sviluppo o di produzione.
Guida Visiva

Prodotti correlati
- Sistema RF PECVD Deposizione Chimica da Vapore Potenziata da Plasma a Radiofrequenza RF PECVD
- Macchina per forni a tubo per deposizione chimica da vapore potenziata al plasma rotante inclinato PECVD
- Sistema di apparecchiature per deposizione chimica da vapore CVD Forno a tubo PECVD con gassificatore a liquido Macchina PECVD
- Sterilizzatore Spaziale al Perossido di Idrogeno VHP H2O2
- Pressa per stampi poligonali per laboratorio
Domande frequenti
- Perché il PECVD utilizza comunemente l'ingresso di potenza RF? Per la deposizione di film sottili di precisione a bassa temperatura
- Cos'è il processo CVD al plasma? Ottenere la deposizione di film sottili a bassa temperatura
- Quali sono le applicazioni del PECVD? Essenziale per semiconduttori, MEMS e celle solari
- Quali sono i componenti del PECVD? Una guida ai sistemi di deposizione di film sottili a bassa temperatura
- Quali sono gli svantaggi della deposizione chimica da vapore potenziata al plasma? Gestire i compromessi della deposizione a bassa temperatura



















